
#Auto turn off battery charger how to
How to make Auto Turn OFF Battery Charger. After measuring the output voltage, add the diode drop (about 0.65V) and bias LM317 accordingly. The charging protocol (how much voltage or current for how long, and what to do when charging is complete) depends on the size and type of the battery being charged. The shut-off voltage point is determined by charging the four cells fully (at 70mA for 14 hours). A battery charger, or recharger, is a device that provides electricity to convert into stored chemical energy for storage in an electrochemical cell by running an electric current through it. Nowadays, 700mAH cells are available in the market, which can be charged at 70 mA for 10 hours. Here, we’ve set the charging voltage at 7.35V for four 1.5V cells. You may determine the charging voltage depending on the NiCd cell specifications by the manufacturer. As a result, relay RL1 de-energises to cut off the charger and red LED1 turns off. As the voltage per cell increasesĬuts off to drive transistor T2 and, in turn, cuts off transistor T3. RL1 and the battery cells start charging. Diode D6 connected between the output of IC1 and battery limits the output voltage to about 6.7V, which is used for charging the battery. Preset VR1 is used for adjusting the bias voltage. In the charging section, regulator IC1 is biased to give about 7.35V. Now even if the pushbutton is released, mains is still available to the primary of the transformer through its normally open (N/O) contacts. This, in turn, turns transistor T1 ‘on’ to energise relay RL1.
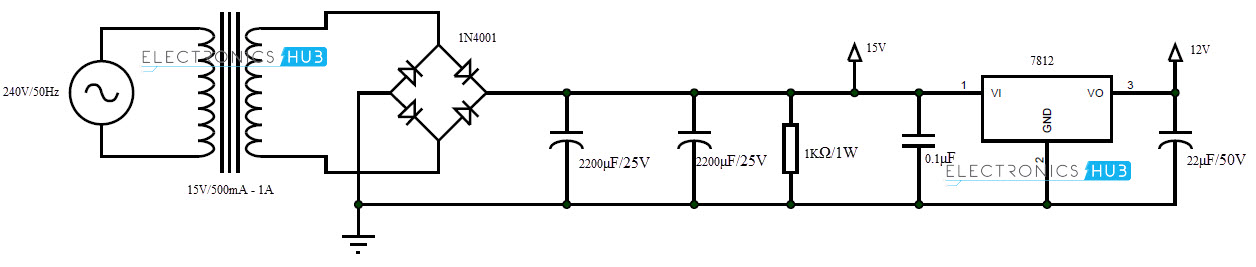
When a current of over 65 mA flows through the 12V line, it causes a voltage drop of about 650 mV across resistor R4 to drive transistor T3 and cut off transistor T2. Resistor R4 (10-ohm, 0.5W) is connected between the emitter and base of transistor T3. Transistor T1 is driven by pnp transistor T2, which, in turn, is driven by pnp transistor T3.
#Auto turn off battery charger driver
The relay driver section uses pnp transistors T1, T2 and T3 (each BC558) to energise electromagnetic relay RL1.Relay RL1 is connected to the collector of transistor T1. When you press switch S1 momentarily, the charger starts operating and the power-on LED1 glows to indicate that the charger is ‘on.’ Regulator IC LM317 (IC1) provides the required 12V DC charging voltage. You can help your phones battery last longer throughout the life of the phone by taking care of the battery and. When the battery voltage increases above 13.5 volts, no more current passes into the battery, so that the voltage at pin3 of IC2 rises and relay turns on.In the AC-to-DC converter section, transformer X1 steps down mains 230V AC to 9V AC at 750 mA, which is rectified by a fullwave rectifier comprising diodes D1 through D4 and filtered by capacitor C1. If the battery takes charge, current to pin 3 of IC2 will be low since most of the current drain occurs into the battery. one NPN transistor such as c1815 for controlling the charging, - relay for cutting off this current path through the battery after fully charged, - 10 kilo-ohm variable resistor connected to the base of the transistor, the variable resistor used for restricting the voltage from. Then connect the battery for charging and switch on S1. this is a circuit of the auto cut off battery charger, it has only:. At this point, relay should energize and Red LED turns on. Slowly adjust VR1 till the input voltage to pin 3 of IC2 raises to 5 volts. Measure the input voltage to pin 3 of IC2. Then connect a fully charged battery/ variable power supply to test points TP observing polarity. Turn the switch S1 to the off position and switch on the power. Charging current to the battery cut off and the relay remains as such since the battery voltage(13.5V or more) keeps the voltage at pin3 of IC2 is higher than that of pin 2.īefore connecting the battery, set the input voltage to IC2 using a fully charged battery or variable power supply. This activates the relay and the contacts break. The circuit is simple and can be divided into AC-to-DC converter, relay driver and charging sections. It can be used to charge partially discharged cells as well. When the terminal voltage of the battery increases to 13.5 volts, pin 3 of IC2 gets higher voltage than pin2 and the output of IC2 becomes high. This Auto Turn-Off Battery Charger Circuit Diagram for series-connected 4-cell AA batteries automatically disconnects from mains to stop charging when the batteries are fully charged. The charging current passes to the battery through the NC (Normally Connected) contacts of the relay. T1 then remains off keeping the relay off. Its inverting input gets 4.7 volt reference voltage from the Zener ZD, while the non inverting input gets an adjustable voltage through the POT VR1.So normally, the inverting input pin 2 gets higher voltage from the Zener (as adjusted by VR1) and output of IC2 remains low.
IC2 (CA3140) is used as a simple voltage comparator to drive the relay.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
